Min Cost to Connect All Points
update Oct 28, 2020
You are given an array points representing integer coordinates of some points on a 2D-plane, where points[i] = [xi, yi].
The cost of connecting two points [xi, yi] and [xj, yj] is the manhattan distance between them: |xi - xj| + |yi - yj|, where |val| denotes the absolute value of val.
Return the minimum cost to make all points connected. All points are connected if there is exactly one simple path between any two points.
Example 1:
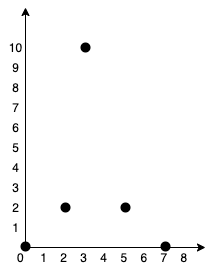

Example 2:
Example 3:
Example 4:
Example 5:
Constraints:
Basic Idea:
1. Kruskal
这道题目是比较典型的MST(最小生成树)的问题,解决MST问题常见的比较好的做法是Kruskal算法,可以做到 O(ElogE) 的时间复杂度。简单来说,Kruskal 就是将所有的边按照weight从小到大排序,从小到大检查每条边相连的点是否已经被加入MST,如果没有,则将其加入。对于这部操作可以使用并查集(Union Find)。所以总体时间复杂度就是对于边排序的时候最慢,即 O(ElogE).
2. Prim
当然也可以使用Prim算法来做,但Prim需要从一个点出发,然后每次relax一个边直到找到所有的点,如果不做优化时间复杂度是非常大的,对于这道题来说是 O(VE). 我们如果使用PriorityQueue来优化的话,理论上可以将时间复杂度做到 O(ElogE). 从一个点出发,每次检查它所有的边,除去已经确定加入MST的点和已经可以使用更短的边连入MST的点,我们将发现的新的点以及其相连边的weight加入PriorityQueue。这样每次PQ出队的就一定是已经确定结果的点,此时我们将它对应边的weight加入结果,然后检查它的所有边,以此类推,直到所有的点都进入了MST为止。因为Java的PQ不支持update,可能会有同一个点因为不同的边被加入pq的情况,但最终时间复杂度可以控制在O(ElogE), 每个点只出队一次,但可以入队不止一次,队列中最多不超过E个node.
Java Code:
Kruskal
Prim
Last updated